10 Best Rear Surround Speakers 2025 in the United States
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.

Our Top Picks
Winner
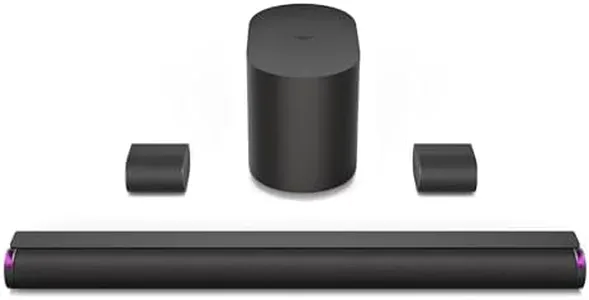
JBL Bar 9.1 - Channel Soundbar System with Surround Speakers and Dolby Atmos, Black
Most important from
1775 reviews
The JBL Bar 9.1 is a versatile soundbar system designed to enhance your home audio experience, especially for movie and music enthusiasts who appreciate immersive surround sound. With a powerful 820W output and built-in Dolby Atmos and DTS:X decoding, it promises a cinema-like audio experience. One of the standout features is its detachable, battery-powered surround speakers, allowing for true wireless surround sound, which is a great advantage for those who dislike cluttered wires. The 10-inch powered subwoofer adds a rich depth to the bass, making action scenes more thrilling and music more enjoyable.
In terms of connectivity, it offers multiple options including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, HDMI, and optical connections, making it compatible with a wide range of devices. The included calibration feature helps tailor the sound to your room, ensuring you get the best audio experience regardless of placement.
There are a few considerations to keep in mind. Although the sound quality is impressive, the system may require some setup and troubleshooting for optimal performance. The surround speakers need recharging, which might be inconvenient for users who prefer plug-and-play systems. Additionally, while the 4K pass-through with Dolby Vision is a nice touch for modern setups, it may not appeal to everyone, particularly those who don’t use the latest technology. It may not be suitable for smaller rooms due to its size and power, but for users looking for a dedicated surround sound system that can fill larger spaces and provide an outstanding audio experience, this soundbar system is a strong contender.
Most important from
1775 reviews
VIZIO 5.1 Soundbar, Wireless Subwoofer, Surround Sound w/Dolby Atmos & DTS:X, Bluetooth Speaker, QuickFit™ Compatible – SV510M-08 (New, 2024 Model)
Most important from
1270 reviews
The VIZIO 5.1 Soundbar SE is a versatile home audio system designed to deliver an immersive surround sound experience, particularly suited for medium to large-sized rooms. With support for Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, this soundbar offers dynamic, high-impact sound. It includes three full-range speakers within the soundbar, two surround speakers, and a wireless subwoofer to ensure a full-bodied audio experience.
The soundbar achieves high sound levels with a sensitivity of 96dB and a maximum output power of 180 Watts, making it powerful enough for most home entertainment setups. Connectivity options are robust, featuring Bluetooth and HDMI eARC, although it does lack an optical output. The VIZIO mobile app provides additional control and customization options, although it does require a VIZIO account.
One notable drawback is that the soundbar remote is sold separately, which might be inconvenient for some users. Mounting is made simple with the QuickFit design, especially for those with compatible VIZIO TVs. The soundbar is not waterproof and has a wired subwoofer, which may limit placement options. This VIZIO soundbar is a strong contender for enhancing TV audio with a full surround sound setup, offering good connectivity and control options, though it requires additional purchases for full functionality.
Most important from
1270 reviews
LG S80QR 5.1.3ch Sound bar with 4ch Rear Speakers, Center Up-Firing, Dolby Atmos DTS:X, Works with Airplay2, Spotify HiFi, Alexa, High-Res Audio, Synergy TV, Meridian
Most important from
511 reviews
The LG S80QR 5.1.3ch soundbar system offers a robust setup for anyone looking to enhance their home cinema experience. With 4-channel rear speakers and a subwoofer, it promises truly immersive surround sound. Notable features include Dolby Atmos and DTS:X technology, which deliver a 3D sound experience. The center up-firing speaker improves voice clarity, making it ideal for dialogue-heavy content. Meridian Audio Technology and High-Res Audio ensure premium sound quality, and its IMAX Enhanced certification means it's built for movie enthusiasts.
The system is highly versatile, compatible with Airplay2, Spotify HiFi, Alexa, and various other AI platforms, allowing for seamless control and integration with other devices. It's particularly designed to complement LG TVs, offering easy control via the LG TV remote and enhanced sound quality through LG’s sound engine. For gamers, the system provides enhanced connectivity with game consoles, including features like Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM) to improve gaming performance.
However, the setup is quite heavy at 49.9 pounds, which may be cumbersome for some users to handle. Additionally, while it offers wireless subwoofer connectivity, the subwoofer itself is not wireless and needs to be wired, which might limit placement flexibility. The system is not water-resistant, so it should be kept away from moisture. Despite these minor drawbacks, the LG S80QR is a strong contender in the rear-surround-sound category, offering a rich feature set and high-quality audio performance, especially for those with compatible LG TVs.
Most important from
511 reviews
Buying Guide for the Best Rear Surround Speakers
Choosing the right rear-surround speakers can significantly enhance your home theater experience by providing immersive sound that makes you feel like you're part of the action. To make an informed decision, it's important to understand the key specifications and how they align with your needs and preferences. Here are the main specs to consider when selecting rear-surround speakers.FAQ
Most Popular Categories Right Now